A Novel Screening Tool System for Depressive Disorders using Social Media and Artificial Neural Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18201/ijisae.2022.274Keywords:
depression, social media, Twitter, ANN, SVM, Logistic Regression, KNNAbstract
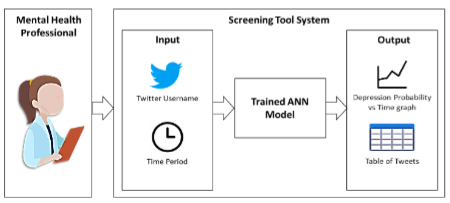
Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders with over 264 million people suffering from it. Improvement in screening depressive disorders can lead to earlier treatment. However, some of the depression screening tools today have constraints and could be difficult to administer due to a lack of cooperation between patient and professional. It is indicated in some studies that there is a correlation between frequent use of social media and increased depression. With this finding, the authors aimed to develop a novel screening tool system incorporated with an artificial neural network that analyzes the patient’s tweets. A design of the screening tool software application was proposed, and an ANN model was developed using a dataset curated from Kaggle. The dataset was cleaned, and features were extracted using the TF-IDF approach. PCA was also used to lessen the number of features for faster training and testing time. Four algorithms were used in training - SVM, Logistic Regression, Perceptron, and KNN. Even though PCA lessens the time for training and testing, it didn’t greatly affect the performance of each model. The SVM model achieved the best performance followed by the Perceptron model. Both the SVM model and the Perceptron model achieved the highest accuracy (98%), but the SVM model achieved better results on the other parameters. However, the SVM model is very slow which prompted the authors to choose the Perceptron model that has a faster speed.
Downloads
References
"Depression", Who.int, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/health-topics/depression. [Accessed: 12- Nov- 2021]
"Depression: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment", Cleveland Clinic, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9290-depression. [Accessed: 12- Nov- 2021]
H. Keshavarz, D. Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D. Streiner, R. Maureen, U. Ali, H. Shannon and P. Raina, "Screening for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis", CMAJ Open, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. E159-E167, 2013.
K. Molebatsi, K. Motlhatlhedi and G. Wambua, "The validity and reliability of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for screening depression in primary health care patients in Botswana", BMC Psychiatry, vol. 20, no. 1, 2020.
B. Koekkoek, B. van Meijel and G. Hutschemaekers, ""Difficult Patients" in Mental Health Care: A Review", Psychiatric Services, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 795-802, 2006.
P. Gil, "What Is Twitter & How Does It Work?", Lifewire, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.lifewire.com/what-exactly-is-twitter-2483331. [Accessed: 12- Dec- 2021]
N. Nittle, "Can Social Media Cause Depression?", Verywell Mind, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.verywellmind.com/social-media-and-depression-5085354. [Accessed: 13- Nov- 2021]
V. Palyan, "The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health", Spotlight on Mental Health Research, 2019 [Online]. Available: https://www.spotlightonresearch.com/. [Accessed: 13- Nov- 2021]
S. Wu, " The Relationship Between Social Media Use and Depression in College Students: A Scoping Review ", Undergraduate, UTHealth School of Public Health, 2019.
K. Puukko, L. Hietajärvi, E. Maksniemi, K. Alho and K. Salmela-Aro, "Social Media Use and Depressive Symptoms—A Longitudinal Study from Early to Late Adolescence", International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 17, no. 16, p. 5921, 2020.
I. Valenzuela, J. Puno, A. Bandala, R. Baldovino, R. de Luna, A. De Ocampo, J. Cuello and E. Dadios, "Quality assessment of lettuce using artificial neural network", 2017IEEE 9th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (HNICEM), 2017.
G. K. Gupta and D. K. Sharma, "Depression Detection on Social Media with the Aid of Machine Learning Platform: A Comprehensive Survey," 2021 8th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), 2021, pp. 658-662, doi: 10.1109/INDIACom51348.2021.00116.
N. Mahdy, D. A. Magdi, A. Dahroug, and M. A. Rizka, “Comparative study: Different techniques to detect depression using social media,” Internet of Things—Applications and Future pp. 441-452, 2020, Springer, Singapore
J. T. Wolohan, M. Hiraga, A. Mukherjee, Z. A. Sayyed, and M. Millard, “Detecting linguistic traces of depression in topic-restricted text: Attending to self-stigmatized depression with NLP,” in Proc. Of the First International Workshop on Language Cognition and Computational Models, 2018, pp. 11-21.
A. H. Orabi, P. Buddhitha, M. H. Orabi, and I. Diana, “Deep learning for depression detection of Twitter users,” in Proc. of the Fifth Workshop on Computational Linguistics and Clinical Psychology: From Keyboard to Clinic, June 2018, pp. 88-97.
S. Hassan, S. Hassan and U. Zakia, "Recognizing Suicidal Intent in Depressed Population using NLP: A Pilot Study", 2020 11th IEEE Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), 2020.
K. Katchapakirin, K. Wongpatikaseree, P. Yomaboot and Y. Kaewpitakkun, "Facebook Social Media for Depression Detection in the Thai Community", 2018 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), 2018.
A. Prakash, K. Agarwal, S. Shekhar, T. Mutreja and P. S. Chakraborty, "An Ensemble Learning Approach for the Detection of Depression and Mental Illness over Twitter Data," 2021 8th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), 2021, pp. 565-570.
A. H. Uddin, D. Bapery and A. S. M. Arif, "Depression Analysis from Social Media Data in Bangla Language using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network Technique," 2019 International Conference on Computer, Communication, Chemical, Materials and Electronic Engineering (IC4ME2), 2019, pp. 1-4.
M. Garg, "Sentimental Analysis for Tweets", Kaggle.com, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/gargmanas/sentimental-analysis-for-tweets. [Accessed: 13- Nov- 2021]
J. Brownlee, "Train-Test Split for Evaluating Machine Learning Algorithms", Machine Learning Mastery, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://machinelearningmastery.com/train-test-split-for-evaluating-machine-learning-algorithms/. [Accessed: 06- Feb- 2022]
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Arnie Mae M. Baes, Aunhel John M. Adoptante, John Carlo A. Catilo, Patrick Kendrex L. Lucero, Janice F. Peralta Peralta, Anton Louise Pernez de Ocampo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.









