Measuring Digitalization of Talent Acquisition Practices And identifying Critical Positions with Employee Branding and Mediating the Role of Technology Resources Strategy
Keywords:
Digitalization, Talent Acquisition, Learning process, company tactics, TechnologyAbstract
This article examined the issues surrounding talent acquisition and how employer branding might assist in resolving some of them. In a competitive environment, organizations struggle to retain skilled and youthful employees. As a result, firms must implement training and development opportunities to retain personnel. With the continuous change of technology in human resources especially in talent acquisition, this study argues that it should not necessarily change HR orientation towards its approach to recruiting practices.
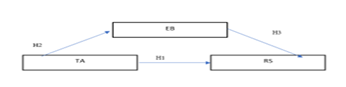
The purpose of this research is to look at the impact of talent management (TM) and identify critical positions with employee branding, as well as the role of resource strategy as a mediator. Human Resources departments will have to evaluate and develop innovative methods of working to develop individualized programs for recognizing and engaging people in a continuous learning process. This strategy should become the core of the organization's future culture. The study aims to investigate the topics of employer branding and talent acquisition, as well as the company's tactics, and the data were analyzed using smartPLS-3 software and the PLS-SEM model. Findings reveal that the employees seem to be satisfied with the Talent Acquisition Procedure. A five-component scale with a some-object measurement model has been verified inside the study. This study presents an empirical model to help readers better comprehend the link. The paper identifies recent critical issues in talent management.
Downloads
References
Anwar, A., Nisar, Q.A., Khan, N.Z.A. and Sana, A., 2014. Talent management: Strategic priority of organizations. International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies, 9(3), p.1148. doi: 36456511/IJIAS-14-271-10_1
Dhanabhakyam, M. and Kokilambal, K., 2014. A study on existing talent management practice and its benefits across industries. International Journal of Research in Business Management, 2(7), pp.23-36.
Srivastava, M.K. and Sharma, M.S., Talent Retention Management: Must for robust Corporate growth, ISSN 2328-3734, 7-11
Rabbi, F., Ahad, N., Kousar, T. and Ali, T., 2015. Talent management as a source of competitive advantage. Journal of Asian business strategy, 5(9), pp.208-214. DOI: 10.18488/journal
Shafieian, G., 2014. Defining talent management components. Advanced Computational Techniques in Electromagnetics, 2014, pp.1-7. doi: /doi.org/10.5899/2014/
Das, G., 2017. Talent Acquisition: It’s evolving Pattern. Social Sciences, 6(01). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21013/jmss.v6.n1.p7
Mensah, J.K., 2015. A “coalesced framework” of talent management and employee performance: For further research and practice. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. DOI:10.1108/IJPPM-07-2014-0100
Kumudha, A. and Priyadarshini, S., 2016. A Conceptual study on challenges and Innovations in Talent Acquisition Process. International Journal of Advance Research in computer science and management studies, 4(1), pp.168-173.
Sekhara, K., 2016. A study on talent acquisition through social media: an exploration, International Conference On Science And Technology, pp 915- 921, doi:/doi.org/10.978.81/932074/0/6
Tripathy, M.S., 2014. Talent acquisition a key factor to overcome new age challenges and opportunities for human resource management. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16(12), pp.39-43. Doi: https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol16-issue12/Version-2/F0161223943.pdf
Srivastava, M.K. and Sharma, M.S., Talent Retention Management: Must for robust Corporate growth. 2017, SSN (Print): 2328-3734, ISSN (Online): 2328-3696, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3688. 7-10
Parthasarathy, M. and Pingle, S., 2014. Study of talent acquisition practices—A review on global perspective. International Journal of Emerging Research in Management & Technology, 3(11), pp.80-85.
Yasin, M., 2017. Talent Mapping/Assessment: Picturizing Talent in Organization. International Journal of Business and Applied Social Science, 3(11).
Sireesha P., Leela K. G., 2014, Talent Management: A Critical Review, IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-ISSN: 2278-487X, p-ISSN: 2319-7668. DOI: 10.9790/487X-17841621
Sequeira, A., Attupuram, P.J. and Gopalakrishnan, S., 2015. Talent acquisition process in a multinational company: A case study. Social Science Research Network.
Kamjula, N., 2012. Talent Management-A Strategic Human Resource Challenge. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 3, pp.1-17.
Collings, D.G., Scullion, H. and Caligiuri, P. eds., 2019. Global talent management. New York: Routledge. DOI: 10.1016/j.jwb.2009.09.011
Wiblen, S., Dery, K. and Grant, D., 2012. Do you see what I see? The role of technology in talent identification. Asia pacific journal of human resources, 50(4), pp.421-438.
Karumuri, V. and Kore, G., 2021. Effective Talent Management Practices: A. Eprajournals. Com, no. June, pp.32-35. 7, (1)ISSN: 2462-1935 32-38
Dixit, S. and Dean, A., 2018. The impact of talent management on job satisfaction and employee performance in public sector banks of Rajasthan. International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts, 6(1), pp.425-435.
Ansar, N. and Baloch, A., 2018. Talent and talent management: definition and issues. IBT Journal of Business Studies (IBTJBS), 14(2).
Jose, S., 2019. Innovation in recruitment and talent acquisition: A study on technologies and strategies adopted for talent management in IT sector. International journal of marketing and human resource management, 10(2), pp.1-8.
Pandita, D., 2019. Talent acquisition: analysis of digital hiring in organizations. SAMVAD, 18, pp.66-72.
Sajeewani K., K. G. G. (2020) “TALENT ACQUISITION AS A STRATEGIC TOOL OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE”, PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences, 6(01), pp. 140–156. doi: 10.20319/pijss.2020.61.14156.
Van Dijk, H.G., 2008. The talent management approach to human resource management: attracting and retaining the right people. Journal of Public Administration, 43(si-1), pp.385-395.
Sang, S., Lee, J. D., & Lee, J. (2010). E-government adoption in Cambodia: a partial least squares approach. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 4(2), 138-157.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd Ed.). New York: Routledge.
Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Modern methods for business research, 295(2), 295-336.
Falk, R. F., & Miller, N. B. (1992). A primer for soft modeling. University of Akron Press.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. Journal of Marketing theory and Practice, 19(2), 139-152.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long range planning, 46(1-2), 1-12.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





