An Efficient Low Complexity Salt & Pepper Noise Detection Method
Keywords:
Impulse noise, Image restoration, salt & pepper noise, Morphological filtering.Abstract
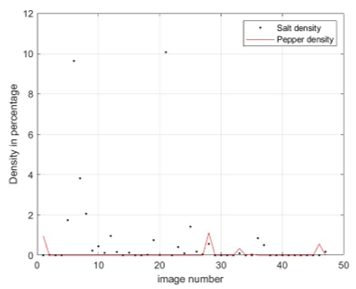
A new impulse noise detection algorithm is proposed in this paper. The most popular method for detection of impulse noise is to classify every pixel with intensity 0 or 255 as noise. Other techniques involve the detection of noise candidates in the first stage followed by false-positive reduction process in the second stage. Both types of techniques have some problems such as the first approach fails to distinguish between a noisy pixel and pure white or black background region. The second type detection algorithm often results in the detection of an unwanted amount of false positives. They also demand more CPU elapsed time. The proposed method is a two-stage impulse noise detector that first detects all the true positives along with false positives that are the result of the appearance of pure white or pure black uniform regions in the image. It then applies morphological operators such as erosion and pixel connectivity to avoid the detection of uniform regions as noisy pixels. Simulation results show that the proposed impulse noise detector method outperformed existing noise detection methods. The proposed method can be applied as an initial noise detection step for the removal of salt & pepper noise using any spatial filter.
Downloads
References
F. Russo, “Edge detection in noisy images using fuzzy reasoning,” IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 1102-1105, May 1998.
E. Abreu, M. Lightstone, S. K. Mitra, and K. Arakawa, “A new efficient approach for the removal of impulse noise from highly corrupted image,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 1012-1025, June 1996.
H. L. Eng, and K. K. Ma, “Noise adaptive soft-switching median filter,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 242-251, Feb. 2001.
T. Wang, J. Qiu, S. Fu, and W. Ji, “Distributed fuzzy H∞ filtering for nonlinear multirate networked double-layer industrial processes,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 5203-5211, Oct. 2016.
P. Civicioglu, “Using uncorrupted neighborhoods of the pixels for impulsive noise suppression with ANFIS,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 759-773, Mar. 2007.
S. Kovaf, J. Valouch, H. Urbančoková, and M. Adámek, “Electromagnetic interference of CCTV,” IEEE International Conference on Information and Digital Technologies, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 172-177, Aug. 2015.
Q. Zhang, R. K. Ward, and J. Du, “Impulse noise correction in TV transmission,” IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, vol. 41, no. 3, pp. 731-737, Aug. 1995.
T. Lin, and P. T. Yu, “Salt-pepper impulse noise detection and removal using multiple thresholds for image restoration,” Journal of Information science and Engineering, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 189-198, Jan. 2006.
V. P. Ananthi, P. Balasubramaniam, and P. Raveendran, “Impulse noise detection technique based on fuzzy set,” IET Signal Processing, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 12-21, Feb. 2018.
M. Biswas, “Impulse Noise Detection and Removal Method Based on Modified Weighted Median,” International Journal of Software Innovation, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 38-53, 2020.
N. Iqbal, S. Ali, I. Khan, and B. M. Lee, “Adaptive edge preserving weighted mean filter for removing random-valued impulse noise,” Mdpi Symmetry, vol. 11, no. 3, 2019.
K. Pritamdas, K. M. Singh, and L. L. Singh, “An adaptive switching filter based on approximated variance for detection of impulse noise from color images,” SpringerPlus, vol. 5, no. 1, 2016.
U. Erkan, L. Gökrem, and S. Enginoglu, “Different applied median filter in salt and pepper noise,” Elsevier Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 789-798, 2018.
S. K. Sathua, A. Dash, A. Behera, “Removal of salt and pepper noise from gray-scale and color images: an adaptive approach,” Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 117-126, 2017.
U. Ghanekar, “A novel impulse detector for filtering of highly corrupted images,” World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, vol. 14, pp. 353–355, 2008.
H. Ibrahim, T. F. Ng, and S. H. Teoh, “An efficient implementation of switching median filter with boundary discriminative noise detection for image corrupted by impulse noise,” Scientific Research and Essays, vol. 6, no. 26, pp. 5523–5533, 2011.
S. Khan, and D. H. Lee, “An adaptive dynamically weighted median filter for impulse noise removal,” EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, vol. 2017, no. 1 , 2017.
A. K. Samantaray, P. Kanungo, and B. Mohanty, “Neighbourhood decision based impulse noise filter,” IET Image Processing, vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 1222-1227, 2018.
H. Ma, and Y. Nie, “A two-stage filter for removing salt-and-pepper noise using noise detector based on characteristic difference parameter and adaptive directional mean filter,” PloS one, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. e0205736-1- e0205736-24, 2018.
M. A. Almomani, S. Basri, and A. R. Gilal, ‘‘Empirical study of software process improvement in Malaysian small and medium enterprises: The human aspects,’’ J. Softw. Evol. Process, vol. 30, no. 10, p. e1953, Oct. 2018.
Edge Detector Comparison. Accessed: Jan. 27. 2022. [Online]. Available: http://www.eng.usf.edu/cvprg/edge/edge_detection.html.
A. R. Gilal, J. Jaafar, S. Basri, M. Omar, and M. Z. Tunio, “Making Programmer Suitable for Team-Leader: Software Team Composition Based on Personality Types,” in International Symposium on Mathematic,
M. Z. Tunio, H. Luo, C. Wang, F. Zhao, A. R. Gilal, and W. Shao, “Task Assignment Model for crowdsourcing software development: TAM,” J. Inf. Process. Syst., 2018.
J. Jaafar, A. R. Gilal, M. Omar, S. Basri, I. A. Aziz, and M. H. Hasan, A Rough-Fuzzy Inference System for Selecting Team Leader for Software Development Teams, vol. 661. 2018.
S. M. Jameel, A. R Gilal, S. S. Hussain Rizvi, M. Rehman, and M. A. Hashmani, “Practical Implications and Challenges of Multispectral Image Analysis,” in 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies: Idea to Innovation for Building the Knowledge Economy, iCoMET 2020, 2020.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





