Minimization of Makespan and Energy Consumption in Task Scheduling in Heterogeneous Cloud Environment
Keywords:
Cloud computing, energy consumption, makespan reduction, task scheduling, cloudsimAbstract
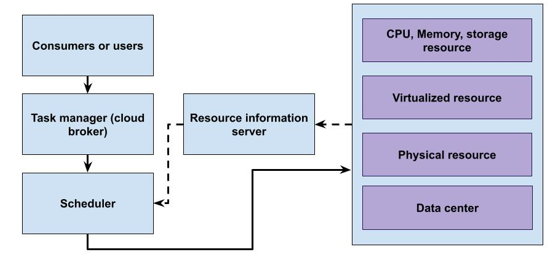
In today's IT industry, cloud computing is one of the technologies that is increasingly being used for regular corporate operations. The cloud is becoming more and more popular among businesses and research communities due to its many benefits, including on-demand self-service, quality of service, pay-per-usage pricing, virtualization, and elasticity. This research propose novel technique in makespan reduction with energy consumption for task scheduling. Here the cloud environment task scheduling for makespan reduction is carried out using gravitational grey wolf hybrid cuckoo scheduling. The simulation is suggested in the cloudsim programming environment, and the outcomes demonstrated the value of the energy-minimizing and makespan parameters. The simulation is suggested in the cloudsim programming environment, and the outcomes demonstrated the value of the energy-minimizing and makespan parameters. Proposed technique attained makespan of 67%, energy efficiency of 96%, execution speed of 79%, resource utilization of 63%, average waiting time of 66% for 500 number of tasks.
Downloads
References
Shukla, D. K., Kumar, D., & Kushwaha, D. S. (2021). Task scheduling to reduce energy consumption and makespan of cloud computing using NSGA-II. Materials Today: Proceedings.
Azizi, S., Shojafar, M., Abawajy, J., & Buyya, R. (2022). Deadline-aware and energy-efficient IoT task scheduling in fog computing systems: A semi-greedy approach. Journal of network and computer applications, 201, 103333.
Mangalampalli, S., Swain, S. K., & Mangalampalli, V. K. (2022). Multi Objective Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing Using Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47(2), 1821-1830.
Ibrahim, I. M. (2021). Task scheduling algorithms in cloud computing: A review. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(4), 1041-1053.
Mangalampalli, S., Swain, S. K., & Mangalampalli, V. K. (2021). Prioritized Energy Efficient Task Scheduling Algorithm in Cloud Computing Using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Wireless Personal Communications, 1-17.
Mukherjee, D., Nandy, S., Mohan, S., Al-Otaibi, Y. D., & Alnumay, W. S. (2021). Sustainable task scheduling strategy in cloudlets. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 30, 100513.
Emami, H. (2022). Cloud task scheduling using enhanced sunflower optimization algorithm. ICT Express, 8(1), 97-100.
Ijaz, S., Munir, E. U., Ahmad, S. G., Rafique, M. M., & Rana, O. F. (2021). Energy-makespan optimization of workflow scheduling in fog–cloud computing. Computing, 103(9), 2033-2059.
Shukri, S. E., Al-Sayyed, R., Hudaib, A., & Mirjalili, S. (2021). Enhanced multi-verse optimizer for task scheduling in cloud computing environments. Expert Systems with Applications, 168, 114230.
Mubeen, A., Ibrahim, M., Bibi, N., Baz, M., Hamam, H., & Cheikhrouhou, O. (2021). Alts: An Adaptive Load Balanced Task Scheduling Approach for Cloud Computing. Processes, 9(9), 1514.
Kaur, R., & Laxmi, V. (2022). Performance evaluation of task scheduling algorithms in virtual cloud environment to minimize makespan. International Journal of Information Technology, 14(1), 79-93.
Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, R., Abouhawwash, M., Chakrabortty, R. K., & Ryan, M. J. (2021). EA-MSCA: An effective energy-aware multi-objective modified sine-cosine algorithm for real-time task scheduling in multiprocessor systems: Methods and analysis. Expert systems with applications, 173, 114699.
Nanjappan, M., Natesan, G., & Krishnadoss, P. (2021). An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and black widow optimization approach for optimal resource utilization and task scheduling in a cloud environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 121(3), 1891-1916.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 R. Priyadarshini, Mukil Alagirisamy, N. Rajendran, Arun Kumar Marandi, Vikas Vilasrao Patil, Vivek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





