Gamification Framework for Engagement Design Using Pls-Sem
Keywords:
E-learning, education, children, emotion, socialAbstract
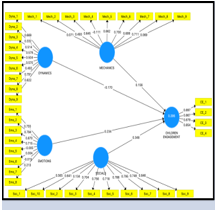
The study's goal is to look into the gamification framework. This research focuses on gamification in e-learning, particularly in early childhood education; the 'what' and 'how' gamification can promote e-learning. Gamification has become popular in the past few years of research in education and business marketing. Early childhood is when brain formation can set the foundation for learning later. The most common scenes are the need to develop a complete and generic framework from a new perspective and its application to different environments in areas such as education and training, business, government, health, and life-day. However, the developed gamification for the business process has suggested more work needs to be done in the gamification area. Even their design framework is yet to be tested and aimed to act as a foundation for future research. Thus, this study aims to develop a gamified framework for children’s engagement design. PLS-SEM was used to analyse the proposed framework. Results show that the framework demonstrates that emotional and social factors substantially link children's engagement. Among the emotions noticed in this research are enjoyment, amusement, and satisfaction. Further research is valuable to explore more possibilities in increasing sustainability and the long-term effects of one gamification learning tool.
Downloads
References
Wittgenstein, L. (2010). Philosophical investigations. John Wiley & Sons.
Nacke, L. E., & Deterding, C. S. (2017). The maturing of gamification research. Computers in Human Behaviour, 450-454.
Arnab, S., Nalla, M., Harteveld, C., & Lameras, P. (2015, September). An inquiry into gamification services: Practices, experiences and insights. In Proceedings of the International Gamification for Business Conference 2015 (pp. 34-45).
Landers, R. N., & Armstrong, M. B. (2017). Enhancing instructional outcomes with gamification: An empirical test of the Technology-Enhanced Training Effectiveness Model. Computers in human behavior, 71, 499-507.
P., Tjondronegoro, D., & Scott-Parker, B. (2017). Driven to drive? Investigating the effect of gamification on learner driver behavior, perceived motivation and user experience. Computers in Human Behavior, 71, 586–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.08.050
Granic, I., Lobel, A., & Engels, R. C. (2014). The benefits of playing video games. American psychologist, 69(1), 66.
Vittrup, B., Snider, S., Rose, K. K., & Rippy, J. (2016). Parental perceptions of the role of media and technology in their young children’s lives. Journal of Early Childhood Research, 14(1), 43-54.
Gelsomini, M., Leonardi, G., & Garzotto, F. (2020, April). Embodied learning in immersive smart spaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1-14).
Mora, A., Riera, D., Gonzalez, C., & Arnedo-Moreno, J. (2015, September). A literature review of gamification design frameworks. In 2015 7th International Conference on Games and Virtual Worlds for Serious Applications (VS-Games) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Dichev, C., Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education: what is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: a critical review. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 14, 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0042-5
Li, X., & Chu, S. K. W. (2020). Exploring the effects of gamification pedagogy on children’s reading: A mixed‐method study on academic performance, reading‐related mentality and behaviors, and sustainability. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52(1), 160–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.13057
Unterhalter, E. (2014). Measuring education for the Millennium Development Goals: reflections on targets, indicators, and a post-2015 framework. Journal of Human Development and Capabilities, 15(2-3), 176-187.
Sitorus, M. B., Ferdiana, R., & Adji, T. B. (2017, August). Designing gamification framework to support social media application based on game elements and cutting-edge technology. In 2017 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS) (pp. 125-130). IEEE.
Zainuddin, Z., Chu, S. K. W., Shujahat, M., & Perera, C. J. (2020). The impact of gamification on learning and instruction: A systematic review of empirical evidence. Educational Research Review, 30, 100326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2020.100326
Dominguez, A., Saenz-de-Navarrete, J., de-Marcos, L., Fernández-Sanz, L., Pagés, C., & Martínez-Herráiz, J.-J. (2013). Gamifying learning experiences: Practical implications and outcomes. Computers & Education, 63, 380–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.12.020
Lee, J., & Hammer, J. (2011). Gamification in Education: What, How, Why Bother? Academic Exchange Quarterly, 15, 1–5. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258697764_Gamification_in_Education_What_How_Why_Bother
Simoes, J. (2015). Using Gamification to Improve Participation in Social Learning Environments. 10.13140/RG.2.1.4253.0328.
Bunchball. (2010). Gamification 101: An Introduction to the Use of Game Dynamics to Influence Behavior. http://jndglobal.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/05/gamification1011.pdf
Hunicke, R., Leblanc, M., & Zubek, R. (2004). MDA: A Formal Approach to Game Design and Game Research. AAAI Workshop - Technical Report, 1.
Kim, B. (2015). Designing Gamification in the Right Way. Library Technology Reports, 51(2), 29–35. https://journals.ala.org/index.php/ltr/article/view/5632
Elverdam, C., & Aarseth, E. (2007). Game Classification and Game Design: Construction Through Critical Analysis. Games and Culture, 2(1), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1555412006286892
Robson, K., Plangger, K., Kietzmann, J. H., McCarthy, I., & Pitt, L. (2016). Game on: Engaging customers and employees through gamification. Business Horizons, 59(1), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2015.08.002
Sweetser, P., & Wyeth, P. (2005). GameFlow: a model for evaluating player enjoyment in games. Computers in Entertainment, 3(3), 3. https://doi.org/10.1145/1077246.1077253
Huang, W. H.-Y., & Soman, D. (2013). A Practitioner’s Guide To Gamification Of Education.
Mohamad, S. N. M., Sazali, N. S. S., & Salleh, M. A. M. (2018). Gamification approach in education to increase learning engagement. International Journal of Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences, 4(1), 22-32.
Raymer, R. (2011, September). Gamification: Using Game Mechanics to Enhance eLearning. https://elearnmag.acm.org/featured.cfm?aid=2031772
Niittylahti, S., Annala, J., & Mäkinen, M. (2021). Student engagement profiles in vocational education and training: a longitudinal study. Journal of Vocational Education & Training, 1-19.
Scager, K., Boonstra, J., Peeters, T., Vulperhorst, J., & Wiegant, F. (2016). Collaborative learning in higher education: Evoking positive interdependence. CBE—Life Sciences Education, 15(4), ar69.
Bond, M., Buntins, K., Bedenlier, S., Zawacki-Richter, O., & Kerres, M. (2020). Mapping research in student engagement and educational technology in higher education: A systematic evidence map. International journal of educational technology in higher education, 17(1), 1-30.
Martin, F., & Bolliger, D. U. (2018). Engagement matters: Student perceptions on the importance of engagement strategies in the online learning environment. Online Learning, 22(1), 205-222.
Cecilio-Fernandes, D., Parisi, M. C. R., Santos, T. M., & Sandars, J. (2020). The COVID-19 pandemic and the challenge of using technology for medical education in low and middle income countries. MedEdPublish, 9(74), 74.
Rianti, A., Hidayati, A. N., Pertamana, D., Andriani, A., & Abdullah, F. (2020). Profiling an ideal teacher. Koli Journal, 1(2), 65-74.
Bellibaş, M. Ş., Polatcan, M., & Kılınç, A. Ç. (2022). Linking instructional leadership to teacher practices: The mediating effect of shared practice and agency in learning effectiveness. Educational management administration & leadership, 50(5), 812-831.
Li, C., & Dewaele, J. M. (2021). How classroom environment and general grit predict foreign language classroom anxiety of Chinese EFL students. Journal for the Psychology of Language Learning, 3(2), 86-98.
Nijhof, S. L., Vinkers, C. H., van Geelen, S. M., Duijff, S. N., Achterberg, E. J. M., van der Net, J., Veltkamp, R. C., Grootenhuis, M. A., van de Putte, E. M., Hillegers, M. H. J., van der Brug, A. W., Wierenga, C. J., Benders, M. J. N. L., Engels, R. C. M. E., van der Ent, C. K., Vanderschuren, L. J. M. J., & Lesscher, H. M. B. (2018). Healthy play, better coping: The importance of play for the development of children in health and disease. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 95(95), 421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.09.024
Dichev, C., & Dicheva, D. (2017). Gamifying education: what is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: a critical review. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0042-5
Bransford, J., Brown, A. L., Cocking, R. R., Donovan, M. S., & Pellegrino, J. W. (2000). How People Learn : Brain, Mind, Experience, and School. National Academy Press.
Hair, J., Hollingsworth, C. L., Randolph, A. B., & Chong, A. Y. L. (2017). An updated and expanded assessment of PLS-SEM in information systems research. Industrial management & data systems.
Thien, L. M. (2020). Assessing a second-order quality of school life construct using partial least squares structural equation modelling approach. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 43(3), 243-256.
Owston, R., & York, D. N. (2018). The nagging question when designing blended courses: Does the proportion of time devoted to online activities matter?. The Internet and Higher Education, 36, 22-32.
Hair Jr, J. F., Howard, M. C., & Nitzl, C. (2020). Assessing measurement model quality in PLS-SEM using confirmatory composite analysis. Journal of Business Research, 109, 101-110.
Purwanto, A., & Sudargini, Y. (2021). Partial least squares structural squation modeling (PLS-SEM) analysis for social and management research: a literature review. Journal of Industrial Engineering & Management Research, 2(4), 114-123.
Bakhsh, M., Mahmood, A., & Sangi, N. A. (2017). Examination of factors influencing students and faculty behavior towards m-learning acceptance: An empirical study. The International Journal of Information and Learning Technology.
Kueh, Y. C., Kuan, G., Morris, T., & Naing, N. N. (2017). Confirmatory factor analysis of the Malay version of the recreational exercise motivation measure. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities, 25(2).
Ab Hamid, M. R., Sami, W., & Sidek, M. M. (2017, September). Discriminant validity assessment: Use of Fornell & Larcker criterion versus HTMT criterion. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 890, No. 1, p. 012163). IOP Publishing.
Sarstedt, M., & Cheah, J. H. (2019). Partial least squares structural equation modeling using SmartPLS: a software review.
Osteen, P., & Bright, C. L. (2010). Effect sizes and intervention research.
Poondej, C., & Lerdpornkulrat, T. (2019). Gamification in e-learning: A Moodle implementation and its effect on student engagement and performance. Interactive Technology and Smart Education, 17(1), 56-66.
Leung, A. C. M., Santhanam, R., Kwok, R. C. W., & Yue, W. T. (2022). Could Gamification Designs Enhance Online Learning Through Personalization? Lessons from a Field Experiment. Information Systems Research.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





