Optimal Process of Video Stabilization Using Hybrid RANSAC-MSAC Algorithm
Keywords:
360° videos, eeded-Up Robust-Features, Feature detection, RANSAC, MSACAbstract
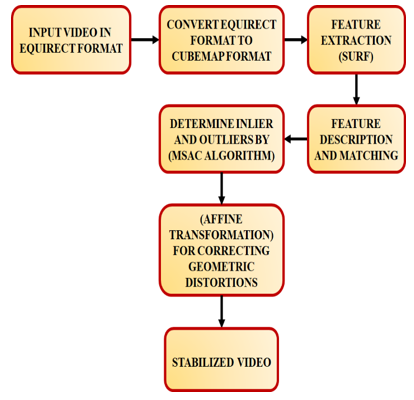
The diversity and amount of cameras are growing as these sorts of cameras are used more frequently, with people filming videos in a variety of settings. Trying to keep the camera stable and prevent shaking is not always simple, especially when using a handheld camera to record motion such as a walking tour or mountain bike ride. So far the majority of video stabilization technology has been created for recording video with a limited field of view, such as conventional videos shot with a smartphone, and it employs methods that don't translate well to 360-degree films. The architecture used by the majority of current video stabilization algorithms aid in attaining various benefits: they track gestures in the video, fit a motion model, smooth the motion, and then generate the stabilized output frames. Consequently, a feature extraction module is included in the video stabilization, and there are various ways to extract the feature. The fact that the SURF (Speeded-Up Robust-Features) is invariant to scale, rotation, translation, illumination, and blur makes them the most suitable techniques for feature detection and matching. To perform reliable estimation of inliers and outliers, hybridized RANSAC (Random sample consensus) and MSAC (M- estimator sample consensus) approaches are proposed in this work. Following this, a matched point pairs are fitted into an affine transformation model, thereby estimating the interframe motion.
Downloads
References
A. Luchetti, M. Zanetti, D. Kalkofen and De Cecco, M., “Stabilization of spherical videos based on feature uncertainty”, The Visual Computer, pp. 1–14, 2022.
M. Zhao and Q. Ling, “A robust traffic video stabilization method assisted by foreground feature trajectories”, IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 42921–42933, 2019.
A. Luchetti, M. Zanetti, D. Kalkofen and M. De Cecco, “Stabilization of spherical videos based on feature uncertainty”, The Visual Computer, pp. 1–4, 2022.
T. Ma, Y. Nie, Q. Zhang, Z. Zhang, H. Sun and G. Li, “Effective video stabilization via joint trajectory smoothing and frame warping”, IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 3163–3176, 2019.
T. Ma, Y. Nie, Q. Zhang, Z. Zhang, H. Sun et al., “Effective video stabilization via joint trajectory smoothing and frame warping”, IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 3163-3176, 2019.
H. Jiang, G. Jiang, M. Yu, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang et al., “Cubemap-based perception-driven blind quality assessment for 360-degree images”, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 30, pp. 2364–2377, 2021.
G. de A. Roberto, N. Birkbeck, I. Janatra, B. Adsumilli and P. Frossard, Multi-feature 360 video quality estimation”, IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 2, pp. 338–349, 2021.
X. Chen, A. T. Z. Kasgari and W. Saad, “Deep learning for content-based personalized viewport prediction of 360-degree VR videos”, IEEE Networking Letters, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 81 – 84, 2020.
P. V. Rouast and M. T. P. Adam , “Learning deep representations for video-based intake gesture detection”, IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 1727–1737, 2020.
M. K. Asha Paul, J. Kavitha and P. A. J. Rani, “Key-frame extraction techniques: a review”, Recent Patents on Computer Science, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 3–16, 2018.
E. Hato and M. E. Abdulmunem, “Fast algorithm for video shot boundary detection using SURF features”, In 2019 2nd Scientific Conference of Computer Sciences (SCCS), pp. 81–86, 2019.
D. Mistry and A. Banerjee, “Comparison of feature detection and matching approaches: SIFT and SURF”, GRD Journals-Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 7–13, 2017.
Y. Feng, “Mobile terminal video image fuzzy feature extraction simulation based on SURF virtual reality technology”, IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 156740–156751, 2020.
J. Li, T. Xu and K. Zhang, “Real-time feature-based video stabilization on FPGA”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 907–919, 2017.
L. Zhang, Q-K. Xu and H. Huang, “A global approach to fast video stabilization”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 225–235, 2017.
T. N. Shene, K. Sridharan and N. Sudha, “Real-time SURF-based video stabilization system for an FPGA-driven mobile robot”, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 63, no. 8, pp. 5012–5021.
Y. Nie, T. Su, Z. Zhang, H. Sun and G. Li, “Dynamic video stitching via shakiness removing”, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 164–178, 2018.
C. Song, H. Zhao, W. Jing and H. Zhu, “Robust video stabilization based on particle filtering with weighted feature points”, IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 570 – 577, 2012.
S. Liu, B. Xu, C. Deng, S. Zhu, B. Zeng et al., “A hybrid approach for near-range video stabilization”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 27, no. 9, pp. 1922–1933, 2017.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 S. Afsal, Arul Linsely

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





