Electrocardiogram Signal Classification for Diagnosis Sudden Cardiac Death Using 2D CNN and LSTM
Keywords:
Electrocardiogram, sudden cardiac death, CNN, LSTMAbstract
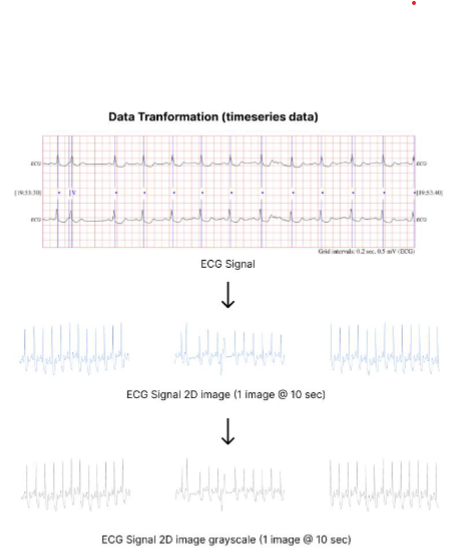
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal evaluation is routinely used in clinics as a significant diagnostic method for detecting sudden cardiac death. Using automated detection and classification methods in the clinic can assist doctors in making accurate and expeditious diagnoses of diseases. In this study, we developed a classification method for sudden cardiac death based on image 2D with the combination of a convolutional neural network and long short-term memory, which was then used to diagnose a normal sinus rhythm and sudden cardiac death. The ECG data of the experiment were derived from the MIT-BIH SCD Holter database and MIT-BIH Normal Sinus Rhythm. 2D CNN model give the best result with average accuracy 96.67%, average sensitivity 100%, average specificity 92.90%, average precision 92.90% and the average F1 score is 97.10% for 1 minutes, 2 minutes and 3 minutes before VF onset.
Downloads
References
Zipes, D. P., & Wellens, H. J. (1998). Sudden Cardiac Death. Circulation, 98(21), 2334–51. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9826323
Lerma, C., & Glass, L. (2016). Predicting the risk of sudden cardiac death. The Journal of physiology, 594(9), 2445-2458.
R. Mrowka, H. Theres, A. Patzak, and G. Baumann, “Alternans-like phenomena due to filtering of electrocardiographic data,” Comput. Cardiol., vol. 25, pp. 725–727, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1109/cic.1998.731976
Ji, Y., Zhang, S., & Xiao, W. (2019). Electrocardiogram classification based on faster regions with convolutional neural network. Sensors, 19(11), 2558.
Zheng, Z., Chen, Z., Hu, F., Zhu, J., Tang, Q., & Liang, Y. (2020). An automatic diagnosis of arrhythmias using a combination of CNN and LSTM technology. Electronics, 9(1), 121.
Bhatt, A., Dubey, S. K., & Bhatt, A. K. (2017). Sudden cardiac arrest prediction using pre-dictive analytics. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering & Systems, 10-3.
Panjaitan, F., Nurmaini, S., Akbar, M., Mirza, A. H., Syaputra, H., & Kurniawan, T. B. (2019, October). Identification of classification method for sudden cardiac death: A review. In 2019 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS) (pp. 93-97). IEEE.
Abrishami, H., Han, C., Zhou, X., Campbell, M., & Czosek, R. (2018). Supervised ECG interval segmentation using LSTM neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (BIOCOMP) (pp. 71-77). The Steering Committee of The World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing (WorldComp).
Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V. K., Sree, V. S., Eugene, L. W. J., Ghista, D. N., & San Tan, R. (2015). An integrated index for detection of sudden cardiac death using discrete wavelet transform and nonlinear features. Knowledge-Based Systems, 83, 149-158.
Fujita, H., Acharya, U. R., Sudarshan, V. K., Ghista, D. N., Sree, S. V., Eugene, L. W. J., & Koh, J. E. (2016). Sudden cardiac death (SCD) prediction based on nonlinear heart rate variability features and SCD index. Applied Soft Computing, 43, 510-519.
Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V. K., Ghista, D. N., Lim, W. J. E., & Koh, J. E. (2015, October). Automated prediction of sudden cardiac death risk using Kolmogorov complexity and recurrence quantification analysis features extracted from HRV signals. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (pp. 1110-1115). IEEE.
Amezquita-Sanchez, J. P., Valtierra-Rodriguez, M., Adeli, H., & Perez-Ramirez, C. A. (2018). A novel wavelet transform-homogeneity model for sudden cardiac death prediction using ECG signals. Journal of medical systems, 42(10), 1-15.
Goldberger, A. L., Amaral, L. A., Glass, L., Hausdorff, J. M., Ivanov, P. C., Mark, R. G., Mietus, J. E., Moody, G. B., Peng, C. K., & Stanley, H. E. (2000). PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation, 101(23), E215–E220. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
Myerburg, R. J. (2008). Cardiac arrest and sudden death. Heart disease: A textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 2, 933-974.
Engelstein, E. D. (1998). Sudden cardiac death. The heart, arteries and veins, 1081-1112.
Furberg, C., Romo, M., Linko, E., Siltanen, P., Tibblin, G., & Wilhelmsen, L. (1977). Sudden coronary death in Scandinavia: a report from Scandinavian Coronary Heart Disease Registers. Acta Medica Scandinavica, 201(1‐6), 553-557.
Wellens, H. J., Schwartz, P. J., Lindemans, F. W., Buxton, A. E., Goldberger, J. J., Hohnloser, S. H., ... & Wilde, A. A. (2014). Risk stratification for sudden cardiac death: current status and challenges for the future. European heart journal, 35(25), 1642-1651.
Deyell, M. W., Krahn, A. D., & Goldberger, J. J. (2015). Sudden cardiac death risk stratification. Circulation research, 116(12), 1907-1918.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





