Improving of Swing up Motion Control Parameters for a Gymnastics Robot Using the Gray Wolf Algorithm
Keywords:
Gymnastic Robot, Gray Wolf Optimization, Inverted Pendulum, Swinging-up ControlAbstract
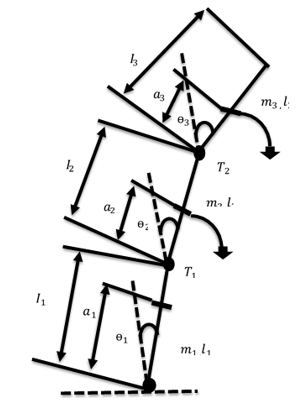
This paper focuses on controlling the swing of a robot consisting of three joints that features free movement of the first joint that causes the system to be both nonlinear system and to develop complex motion. The resulting robot gymnast thus simulates a human trying to swing smoothly from a stable (lower) position to an unstable (upper) position by feeding power to the shoulder and hip joints. The main purpose of this paper is to determine how best to adjust the control signal input to the DC motors in the robot’s “shoulder” and “hip” in order to move these joints into a vertical balanced plane. The Gray Wolf Algorithm (GWO) was adopted as a novel optimisation technique to calculate the optimal values for simulation of the behaviour of the robot in the swing phase, and the ensuing experimental and simulation results suggested that this was successful in managing the robot’s swing.
Downloads
References
E. E. Eldukhri and H. G. Kamil, “Optimisation of swing-up control parameters for a robot gymnast using the Bees Algorithm,” J. Intell. Manuf., vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 1039–1047, Oct. 2015, doi: 10.1007/s10845-013-0848-5
D. LIU and H. YAMAURA, “Giant Swing Motion Control of 3-link Gymnastic Robot with Friction around an Underactuated Joint,” J. Syst. Des. Dyn., vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 925–936, 2011, doi: 10.1299/jsdd.5.925.
E. E. Eldukh E. E. Eldukhri and D. T. Pham, “Autonomous swing-up control of a three-link robot gymnast,” Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng., vol. 224, no. 7, pp. 825–833, Nov. 2010, doi: 10.1243/09596518JSCE948
N. P. Nguyen, H. Oh, Y. Kim, J. Moon, “A nonlinear hybrid controller for swinging-up and stabilizing the rotary inverted pendulum SpringerNature., 2021, doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06317-2
Spong MW, “The Swing Up Control Problem For The Acrobot,” IEEE Control Syst., no. May 1994, pp. 49–55, 1995.
X. Yu and M. Bedillion, “Control for a two-link planar robot with an actuated tail,” ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Proceedings (IMECE), vol. 4A-2018. 2018. doi: 10.1115/IMECE2018-86827.
F. Tajdari, E. Khodabakhshi, M. Kabganian, and A. Golgouneh, “Switching controller design to swing-up a two-link underactuated robot,” 2017 IEEE 4th International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation, KBEI 2017, vol. 2018-Janua. pp. 0595–0599, 2018. doi: 10.1109/KBEI.2017.8324869.
M. Tum, G. Gyeong, Ja. H. Park, and Y. S. Lee2, “Swing-up Control of a Single Inverted Pendulum on a Cart With Input and Output Constraints,” IEEE 2014, doi: 10.5220/0005018604750482.
L. SHAIKHET, “STABILITY OF DIFFERENCE ANALOGUE OF LINEAR MATHEMATICAL INVERTED PENDULUM”, Hindawi, (2005), doi: 10.1155/DDNS.2005.215 .
Hongliang Gao ,1 Xiaoling Li,1 Chao Gao,2 and Jie Wu1 1School“Neural Network Supervision Control Strategy for Inverted Pendulum Tracking Control”, Hindawi Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2021, Article ID 5536573, 14 pages, doi.org/10.1155/2021/5536573.
Y. S. Hussein, H. G. Kamil, A. A. Al-Moadhen, “Robust Hybrid Controller Design to Stabilise an Underactuated Robot Vehicle under Various Input,” Journal of Robotics Volume 2022, Article ID 5477391, 16 pages,doi:10.1155/2022/5477391.
João M. Lopes, Luís Moreira, Cristiana Pinheiro, Daniel Sanz-Merodio, Joana Figueiredo, Cristina P. Santos, and Elena Garcia, “Autonomous swing-up control of a three-link robot gymnast,” Nov.(2019), doi:10.1109@ENBENG.2019.8692531.
M. Yamakita, K. Nonaka, and K. Furuta, “Swing up control of a double pendulum,” American Control Conference. pp. 2229–2232, 1993. doi: 10.23919/acc.1993.4793279.
Y. W. Tseng and J. G. Hsieh, “Optimal control for a family of systems in novel state derivative space form with experiment in a double inverted pendulum system,” Abstract and Applied Analysis, vol. 2013. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/715026.
Boutaina Elkinany ,1 Mohammed Alfidi,1 Redouane Chaibi,2 and Zakaria Chalh 1 1Laboratory T-S “Fuzzy System Controller for Stabilizing the Double Inverted Pendulum”, Hindawi Advances in Fuzzy Systems Volume 2020, Article ID 8835511, 9 pages doi: 10.1155/2020/8835511.
T. Henmi, M. Deng, Ahra Inoue, “Swing-up Control of a Serial Double Inverted Pendulum” American Control Conference Boston, Massachusetts June 30. July 2,2004, doi: 0-7803-8335-4.
M. Bugeja, “Non-linear swing-up and stabilizing control of an inverted pendulum system,” IEEE Region 8 EUROCON 2003: Computer as a Tool - Proceedings, vol. B. pp. 437–441, 2003. doi: 10.1109/EURCON.2003.1248235.
J. L. Sung et al., “Characterizing the Validity of the Inverted Pendulum Model for Quiet Standing,” Journal of Healthcare Engineering, vol. 2021. 2021. doi: 10.1155/2021/8884614.
H. G. Kamil, A. A. Ahmed, A. K. Abbas, “Tuning of Control Motion for a three link robot manipulator using Particle Swarm Optimization Technique,” Journal University of Kerbala , Vol. 15 No.4 Scientific . 2017, doi: KJ1351061512073800.
Dung-Han Lee , lui-Hsiu Hsu, Po-Wen Lin, Te-Hsin Chang, Pei-Chun Lin, “Swing up control of a double pendulum,” 20 17 IEEE, doi: 10.1109/ICCAR.2017.7942681.
A. A Al - Moadhen1, A. M Abdulhussein, H. G Kamil, “Planning and acting framework under robot operating system,” Materials Science and Engineering 433 (2018) 012090 doi:10.1088/1757-899X/433/1/012090
H. G. Kamil, E. E. Eldukhri, and P. A. Uk, “OPTIMISATION OF SWING-UP CONTROL PARAMETERS FOR A ROBOT GYMNAST USING THE BEES ALGORITHM.”
A. Kaveh and P. Zakian, “Improved GWO algorithm for optimal design of truss structures,” Eng. Comput., vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 685–707, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1007/s00366-017-0567-1.
N. Singh and S. B. Singh, “Hybrid Algorithm of Particle Swarm Optimization and Grey Wolf Optimizer for Improving Convergence Performance,” Journal of Applied Mathematics, vol. 2017. 2017. doi: 10.1155/2017/2030489.
P. Saxena and A. Kothari, “Optimal Pattern Synthesis of Linear Antenna Array Using Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm,” International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, vol. 2016. 2016. doi: 10.1155/2016/1205970.
Sen Zhang1 and Yongquan Zhou1,2 1College, “Grey WolfOptimizer Based on Powell Local Optimization Method for Clustering Analysis”, Hindawi 2015, Article ID 481360, 17 pages doi:10.1155/2015/481360.
S. Gholizadeh, “OPTIMAL DESIGN OF DOUBLE LAYER GRIDS CONSIDERING NONLINEAR BEHAVIOUR BY SEQUENTIAL GREY WOLF ALGORITHM,” INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF OPTIMIZATION IN CIVIL ENGINEERING Int. J. Optim. Civil Eng., 2015; 5(4):511-523.
E. Hernández, O. Castillo, and J. Soria, “Optimization of Fuzzy Controllers for Autonomous Mobile Robots Using the Grey Wolf Optimizer,” Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 827. pp. 289–299, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34135-0_20.
M.A.EBRAHIM1, M.E.MOUSA2, E.M. SAID1,3, M.MAHMOUD ZAKY2, S.A.KOTB2 “Optimal Design of Hybrid Optimization Technique for Balancing Inverted Pendulum System”, DOI: 10.37394/23202.2020.19.19.
S. Mirjalili, S. M. Mirjalili, and A. Lewis, “Grey Wolf Optimizer,” Adv. Eng. Softw., vol. 69, pp. 46–61, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





