Extracting Contextual Feature Form Hinglish Short Text by Handling Spelling Variation at Character and Word Level
Keywords:
Pre-Processing, short text, Auto-Encoder, HinglishAbstract
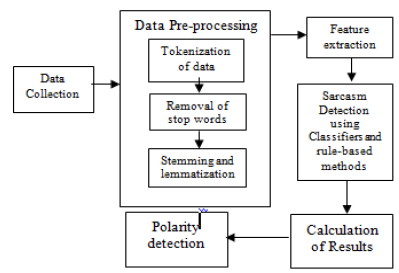
The major purpose of sarcasm detection has been to comprehend the text's evaluation. Sarcasm detection is regarded as one of the most provocations in it, and it has been subject to significant provocation. Irony is a unique manner of expressing information that contradicts a notion and creates confusion. Data pre-processing is one of the main duties performed by most developers. Numerous studies on irony detection use a variety of feature extraction techniques. These studies used a variety of machine learning classification models that includes Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, etc. Precision, recall, and F-score are among the research project results that can be utilized to forecast the most appropriate model. This study discusses numerous methods for detecting sarcasm and irony in text. Extra Tree Classifier and gradient boosting classifier gives the best result having F-Score 95.43 and 95.29 respectively with Wn = 4,Cn = 3 and CWn =4 to detect sarcasm in Hinglish Language.
Downloads
References
Aditya Joshi, Pushpak Bhattacharyya, and Mark J. Carman. 2017. Automatic sarcasm
detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv., 50(5).
Sahil Swami, Ankush Khandelwal, Vinay Singh, Syed Sarfaraz Akhtar, and Manish Shrivastava. A corpus of english-hindi code-mixed tweets for sarcasm detection, (2018).
Shalini, K., Hb, B.G., Kumar, M., Soman, K.P.: Sentiment analysis for code-mixed Indian social media text with distributed representation. In: 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), pp. 1126–1131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2018.8554835.
Mishra, P., Danda, P., Dhakras, P.: Code-mixed sentiment analysis using machine learning and neural network approaches (2018)
Choudhary, N., Singh, R., Bindlish, I., Shrivastava, M.: Sentiment analysis of code-mixed languages leveraging resource rich languages. In: 19th International Conference on Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, 2018, Hanoi, Vietnam (2018).
Pradhan, R., Sharma, D.K. An ensemble deep learning classifier for sentiment analysis on code-mix Hindi–English data. Soft Computing(2022).
R. Bhargava, Y. Sharma and S. Sharma,: Sentiment analysis for mixed script Indic sentences. In: 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Jaipur, India, pp. 524-529(2016).
Patwa, P., Aguilar, G., Kar, S., Pandey, S.J., Pykl, S., Gambäck, B., Chakraborty, T., Solorio, T., & Das, A. SemEval-2020
Task 9: Overview of Sentiment Analysis of Code-Mixed Tweets, (2020).
Mandal, S., Mahata, S.K., & Das, D. Preparing Bengali-English Code-Mixed Corpus for Sentiment Analysis of Indian Languages.(2018)
Banerjee, S., Jayapal, A.K., & Thavareesan, S. NUIG-Shubhanker@Dravidian-CodeMix- FIRE2020: Sentiment Analysis of Code-Mixed Dravidian text using XLNet. Fire(2020)
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Rajshree Singh, Reena Srivastava

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





