Predicting the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases using Machine Learning Techniques
Keywords:
Coronary ailment, Heart disease, ECG, Data mining, Respiratory disappointmentsAbstract
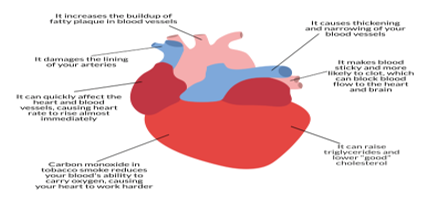
These days, health-related diseases are increasing day by day due to lifestyle and genetics. Especially these days, heart disease is so common that people's lives are at risk. Blood pressure, cholesterol and pulse rate vary from person to person. However, according to proven clinical results, normal blood pressure is 90/120 and cholesterol is 129-100 mg/dL, Pulse 72, fasting blood glucose 100 mg/dL, heart rate 100-60 bpm, normal ECG, main vessel width 25 mm (1 inch) in the aorta only 8 μm in the capillaries. This article looks at the different classification techniques used to predict each person's risk level based on age and gender. Blood pressure, cholesterol, heart rate. A "disease prediction" system based on predictive modeling predicts a user's disease based on the symptoms the user enters into the system. The system analyzes the symptoms that the user provides as inputs and provides disease probabilities as outputs. Disease prediction is done by applying techniques like KNN, Decision tree classifiers, random forest algorithms, and more. This technique calculates the probability of a disease. Therefore, we obtain an average prediction accuracy probability of 86.48%.
Downloads
References
S. F. Dessai, “Intelligent Heart Disease Prediction System Using Probabilistic Neural Network,” no. 5, pp. 38–44, 2013.
E. Y. and C. Kilikcier, “Determination of Patient State from Cardiotocogram using LSSVM with Particle Swarm Optimization and Binary Decision Tree,” Master Thesis, Dep. Electr. Electron. Eng., no. Uludag, 20.
N. S. and D. Singh, “Performance Evaluation of K-Means and Hierarchal Clustering in Terms of Accuracy and Running Time,” Dep. Comput. Sci. Eng. Barkatullah Univ. Inst. Technol., no. Ph.D Dissertation, 2
I. S. F. Dessai, “Intelligent Heart Disease Prediction System Using Probabilistic Neural Network,” no. 5, pp. 38–44, 2013.
T. Karayilan and Ö. Kiliç, “Prediction of Heart disease using neural network,” in 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering, UBMK 2017, 2017, pp. 719–723.
M. Mardiyono, R. Suryanita, and A. Adnan, “Intelligent Monitoring System on Prediction of Building Damage Index using Neural-Network,” TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Comput. Electron. Control., vol. 10, no. 1, p. 155, 2015
N. Guru, A. Dahiya, and N. Rajpal, “Decision support system for heart disease diagnosis using Neural Network,” 2007.
J. S. Singh Navdeep, “No Title,” Intell. Hear. Dis. Predict. Syst. using CANFIS Genet. Algorithm, Int. J. Biol. Med. Sci., no. International Journal of Advance Research, Ideas and Innovations in Technology© 2018, www.IJARIIT.comAll Rights, p. Reserved Page | 987, 2008.
R. G. S. Rajkumar Asha, “No Title,” Diagnosis Hear. Dis. Using Datamining Algorithm, vol. Issue 10 V, no. Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology, p. Page 38, 20
S. Radhimeenakshi and G. M. Nasira, “Prediction of Heart Disease using Neural Network with Back Propagation,” Int. J. Data Min. Tech. Appl., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 19– 22, 2016.
“Prediction of Heart Disease using Artificial Neural Network,” VFAST Trans. Softw. Eng., pp. 102–112, 2019.
Halaudi Daniel M., “Prediction of heart disease using classification algorithms.,” WCSECS, pp. 22–24, 2014
G. S. Kumari Milan, “No Title,” Comp. Study Data Min. Classif. Methods Cardiovasc. Dis. Predict., vol. Vol. 2, no. IJCST Vol. 2, Iss ue2, June 2011, 2011
Z. M. A. Mehta Rupa G. ,Rana Dipti P., “No Title,” A Nov. Fuzzy Based Classif. Data Min. using Fuzzy Discret., no. World Congress on Computer Science and Information, 2008.
X. Y. et Al., “Combination Data Mining Models with New Medical Data to Predict Outcome of Coronary Heart Disease,” Proc. Int. Conf. Converg. Inf. Technol., pp. 868–872, 2007.
Jankowski, J., Floege, J., Fliser, D., Boehm, M., & Marx, N. (2021). Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiological insights and therapeutic options. Circulation, 143(11), 1157-1172
Eckel, R. H., Bornfeldt, K. E., & Goldberg, I. J. (2021). Cardiovascular disease in diabetes, beyond glucose. Cell Metabolism, 33(8), 1519-1545.
S. G. Manoj B, Kumar G, Ramesh G, “Emerging risk factors for cardiovascular diseases: Indian context.,” Indian J Endocrinol Metab, vol. 17, pp. 806–814, 2013.
N. S. and D. Singh, “Performance Evaluation of K-Means and Hierarchal Clustering in Terms of Accuracy and Running Time,” Dep. Comput. Sci. Eng. Barkatullah Univ. Inst. Technol., no. Ph.D Dissertation, 2012
A. A. Shinde, S. N. Kale, R. M. Samant, A. S. Naik, and S. A. Ghorpade, “Heart Disease Prediction System using Multilayered Feed Forward Neural Network and Back Propagation Neural Network,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 166, no. 7, pp. 975– 8887, 2
M. C. and P. M. Franck Le Duff, CristianMunteanb, “Predicting Survival Causes After Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest using Data Mining Method,” Stud. Health Technol. Inform., vol. Vol. 107, no. 2, p. No. 2.
Chaudhary, A., & Garg, P. (2014). Detecting and diagnosing a disease by patient monitoring system. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering And Information Technology, 2(6), 493-499.
Puneet Garg ✌
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Puneet Garg, Neetu Sharma, Sonal, Bharati Shukla

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





