Assessing the Performance of SME and RME Biodiesels through Combustion Simulation for PCCI-DI Constant Speed Engine
Keywords:
HCCI, PCCI, Simulation, Emission reduction, Bio-Diesel, Diesel-RKAbstract
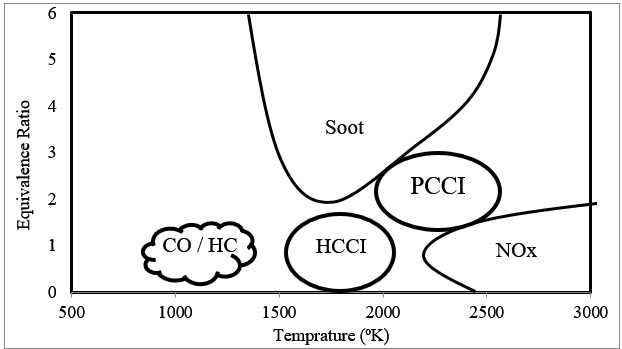
The environmental effect of engine exhaust causing environmental pollution has triggered stringent pollution norms. The two ways of achieving the ever-tightening pollution norms are by combustion improvement on the side engine or the use of after-treatment devices after the emissions are already formed inside the engine. NOx and PM emissions are the two engine emitants that form the engine exhaust apart from CO and HC. To limit these emissions, combustion improvement is proposed. This can be one using different fuels, different combustion methodologies and use of higher pressures for fuel injection for better atomization or the external after-treatment devices. This paper studies two aspects of emission alterations through simulation. The first is the use of SME & RME types of bio-fuels and the use of PCCI combustion approach for the emission improvement. The PCCI approach is used as the HCCI is difficult to control. The assessment is done on the constant speed genset engine as the current research is mainly focused on the vehicle engines alone. Diesel-RK simulation software is used for the pre-injection approach for the PCCI and the bio-fuels of SME & RME. The results shows significant reduction up to 85% can be achieved in particulate matter with use of biodiesels. The overall NOx reduction can be achieved with use of B100 SME. However, the B100 RME gives NOx reduction only at higher loads. With biodiesel, the overall engine efficiency deteriorates. This deterioration is significant at lower loads.
Downloads
References
Al-Dawody, M. F., & Bhatti, S. K. (2014). Experimental and computational investigations for combustion, performance and emission parameters of a diesel engine fueled with soybean biodiesel-diesel blends. In Energy Procedia. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.07.094
Datta, A., & Mandal, B. K. (2016). Impact of alcohol addition to diesel on the performance combustion and emissions of a compression ignition engine. Applied Thermal Engineering. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.047
Datta, A., & Mandal, B. K. (2017). Engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a compression ignition engine operating on different biodiesel-alcohol blends. Energy. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.110
Gowthaman, S., & Sathiyagnanam, A. P. (2018). Analysis the optimum inlet air temperature for controlling homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine. Alexandria Engineering Journal. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2017.08.011
Juttu, S., Mishra, P., Thipse, S. S., Marathe, N. V, & Babu, M. K. G. (2011). Combined PCCI-DI Combustion to Meet EURO-IV Norms on LCV Engine - Experimental and Visulisation Study. In SAE International Journal of Automotive ENGINES (Vol. 26, p. 31). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4271/2011-26-0031
Juttu, S., Thipse, S. S., Marathe, N. V., Babu, G. M. K., & Andersson, A. I. (2009). CFD Study of Combustion Chambers for Lower Engine Exhaust Emissions from Diesel Engines Operated in HCCI and Conventional Diesel Mode. In SAE Technical Papers (Vol. 2009-Janua). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4271/2009-26-0027
Juttu, S., Thipse, S. S., Marathe, N. V., & Gajendra Babu, M. K. (2007). Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI): A New Concept for Near Zero NOx and Particulate Matter (PM) from Diesel Engine Combustion. SAE Technical Papers, 285–294. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4271/2007-26-020
Kuleshov, A., & Grekhov, L. (2013a). Multidimensional optimization of di diesel engine process using multi-zone fuel spray combustion model and detailed chemistry NOx formation model. In SAE Technical Papers. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4271/2013-01-0882
Kuleshov, A., & Grekhov, L. (2013b). Multidimensional Optimization of DI Diesel Engine Process Using Multi-Zone Fuel Spray Combustion Model and Detailed Chemistry NOx Formation Model. In SAE Technical Papers (Vol. 2). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4271/2013-01-0882
Liang, X., Zheng, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., & Yu, H. (2019). A Review of Early Injection Strategy in Premixed Combustion Engines. Applied Sciences 2019, Vol. 9, Page 3737, 9(18), 3737. Retrieved 22 March 2023 from https://doi.org/10.3390/APP9183737
Mansoury, M., Jafarmadar, S., Talei, M., & Lashkarpour, S. M. (2016). Optimization of HCCI ( Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition ) engine combustion chamber walls temperature to achieve optimum IMEP using LHS and Nelder Mead algorithm. Energy, 1–12. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.11.047
Paul, G., Datta, A., & Mandal, B. K. (2014). An experimental and numerical investigation of the performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with jatropha biodiesel. In Energy Procedia. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.07.288
Saxena, S. (2011). Maximizing Power Output in Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engines and Enabling Effective Control of Combustion Timing. University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved from http://digitalassets.lib.berkeley.edu/etd/ucb/text/Saxena_berkeley_0028E_11927.pdf
Tsaousis, P., Wang, Y., Roskilly, A. P., & Caldwell, G. S. (2014). Algae to energy: Engine performance using raw algal oil. In Energy Procedia. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.936
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Hemant A. Kinikar, Amarsingh B. Kanase-Patil , Sukrut S. Thipse , Tushar A. Jadhav

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All papers should be submitted electronically. All submitted manuscripts must be original work that is not under submission at another journal or under consideration for publication in another form, such as a monograph or chapter of a book. Authors of submitted papers are obligated not to submit their paper for publication elsewhere until an editorial decision is rendered on their submission. Further, authors of accepted papers are prohibited from publishing the results in other publications that appear before the paper is published in the Journal unless they receive approval for doing so from the Editor-In-Chief.
IJISAE open access articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This license lets the audience to give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made and if they remix, transform, or build upon the material, they must distribute contributions under the same license as the original.





